Cloud Connector
Introduction
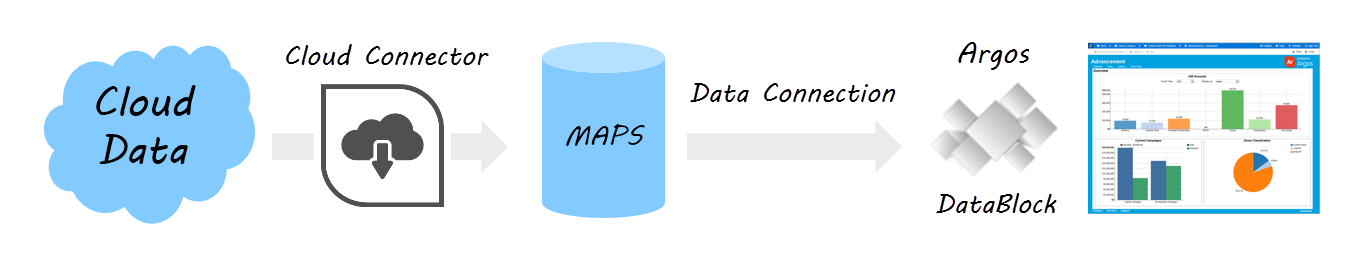
The Cloud Connector provides a way for you to load data from third-party web applications into Argos or other MAPS applications. ADO, Oracle, and MSSQL data connections only support access to SQL-based data sources, and require the ability to log in directly to the database. With the Cloud Connector, you can connect to any data source that provides a RESTful API.
The data source you want to connect to might provide only an API interface, or they may also have created a preexisting web data connector for this purpose. A web data connector is an HTML file that includes JavaScript code that makes the API call to retrieve data from the external source, and then returns it in JSON format that MAPS can understand. The HTML file is hosted on a web server or other location that is visible to MAPS via a URL.
If the data source provides its own HTML interface, you can simply use its URL to create the data connection. If access is via API, a web data connector must be written to make the API call and return the data to MAPS. Once a script has been created, you then set up a Cloud Connector data connection in MAPS, which can be used in the MAPS applications just like any other data connection.
Installation (MAPS Administrator)
Confirm MAPS Version
You will need to be on MAPS 6.0 or later in order to use the Cloud Connector. You
Locate Web Data Connector or Deploy Script Files
The next step is to determine where your data will be coming from, and locate an existing web data connector or create the HTML and JavaScript or other files needed to return the data in JSON format.
- If the third-party source you are connecting to provides their own web data connector that returns data in JSON format, you can simply use that URL to configure the Cloud Connector.
- If a connector is not already available or does not return the data you require, you have the option to create the necessary HTML and JavaScript files yourself.
- Alternatively, Evisions Professional Services can provide a quote for developing a connector that meets your needs.
Test Scripts
Here are some examples of third-party connectors that you can use to test the Cloud Connector.
- OpenStreetMap data: http://jdomingu.github.io/osm-features-wdc/
- USGS Earthquake data: https://tableau.github.io/webdataconnector/Examples/html/earthquakeMultitable.html
- Game of Thrones data: https://stephdietzel.github.io/ConnectorOfIceAndFire/connect.html
Deploy Script Files
Unless you are using an existing connector provided by a third party, you will need to host the HTML and JavaScript files in a location that is available from any machines from which you may be configuring the Cloud Connector.
- One option is to place the script files in the http_files directory of the MAPS Service folder, using the same web server that hosts the eLauncher files. In this case, the URL to the connector would look something like https://myMAPSserver/connector.html where connector.html is the name of the HTML file placed in your http_files directory.
- You may wish to change this path to include a subdirectory.
- You can host the files elsewhere if it is more convenient.
Configure MAPS Data Connection
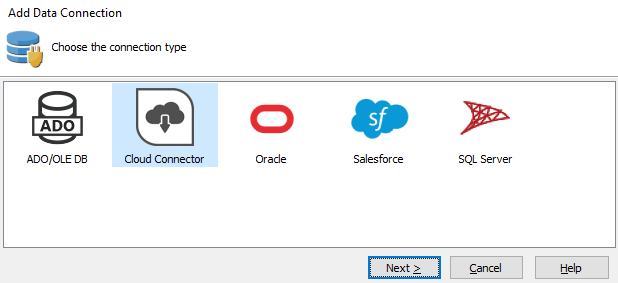
On the Data Connections screen in MAPS Config, create a new data connection and select Cloud Connector as the connection type.
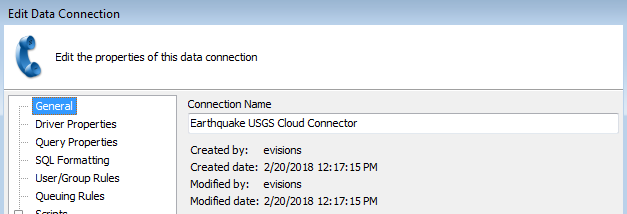
Under General, enter a name for the connection to identify this Cloud Connector.
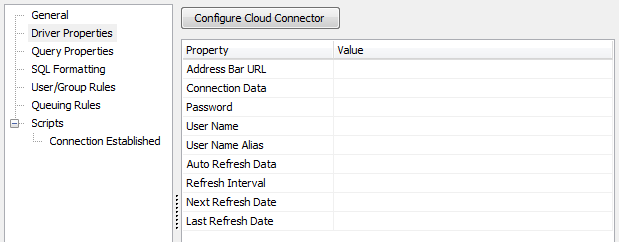
Go to the Driver Properties section and select the Configure Cloud Connector button at the top of the screen above the properties list.
This will open a new window where you enter the Connector URL. This URL is the web address to the HTML file that you set up in the previous step. If you are using a third-party connector, this is the URL that they provide.
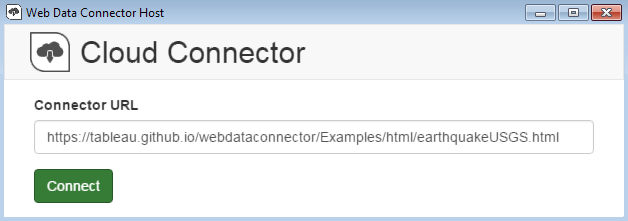
After entering the URL, click the Connect button to attempt to establish a connection.
If successful, you will see the HTML page for the web data connector.

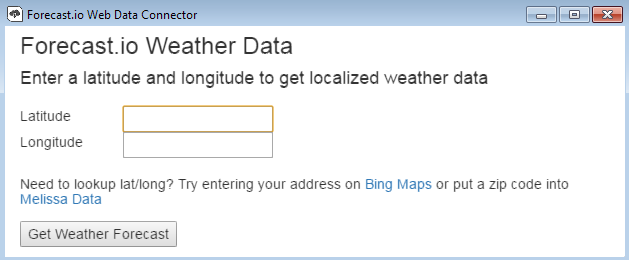
In the examples above, selecting "Get Earthquake Data" or "Get Weather Forecast" will make a request to the third-party connector, which then returns a JSON file to MAPS. The JSON file contains the information that MAPS needs to make API calls to the connector using any specified parameters.
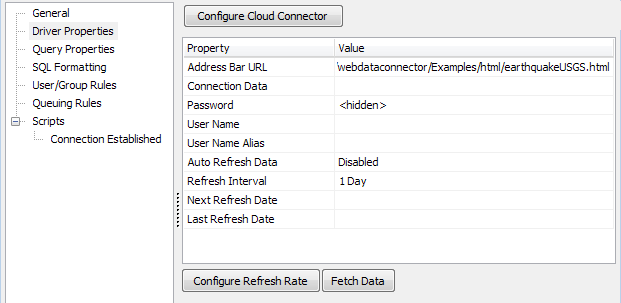
To retrieve data using the connection, select the Fetch Data button under the list of properties. This will create a SQLite database on the MAPS server that contains the data returned by the API call. If successful, you will see the message "Fetch Data Completed".
The JSON and SQLite files for each Cloud Connector are stored in the ..\MAPS\Service\WDC\Connectors folder on the MAPS server.
- If you need to make changes to the URL or parameters you entered, you can use the Reconfigure Cloud Connector button at any point to launch the Configuration dialog again.
- If you want this connection to automatically refresh the data from time to time, use the Configure Refresh Rate button to edit the refresh properties.
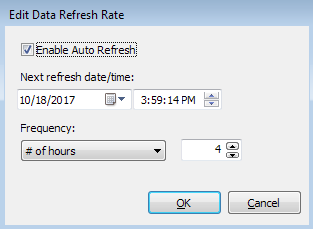
First, check the Enable Auto Refresh box to enable automatic refreshing. Then, enter the next date and time you wish the data to update, and the frequency that you want it to update (every x minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, or years). The data source's API will be called periodically at the scheduled times to pull in the latest data.
You can leave the other data connection properties set to their defaults.
- SQL Formatting - You must leave the SQL Format set to its default of ANSI SQL-92. This option is typically used to specify the type checking when using Free Type queries in Argos, however for the Cloud Connector no type checking is performed.
- User/Group Rules - As with any data connection, you will need to configure which users and groups should have access to the connection. For each user or group, the Cloud Connector uses the connection username and password regardless of what credential source is specified. However, you can still select "Not allowed to connect" for users or groups who should not be able to use this connection. Note that the options to allow insert/update, delete, and non-DML scripts are always disabled for Cloud Connector data connections since the Cloud Connector is only retrieving a snapshot of the data, not performing actions on it.
- Other options such as queuing rules or scripts can be configured as desired.
Finally, don't forget to authorize the new data connection for use with the MAPS applications (Argos, etc.).
The Cloud Connector is now ready for use.
Using the Cloud Connector Data Connection
The Cloud Connector you created can be used in the MAPS applications just like any other data connection. For example, to use this connection as the default connection for an Argos DataBlock, first select your DataBlock, and then choose the Cloud Connector connection from the Associated Connection/Group drop-down.
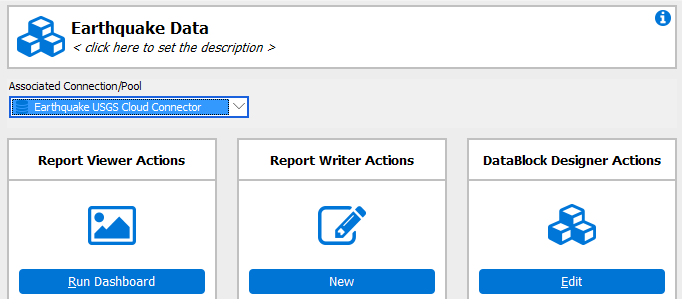
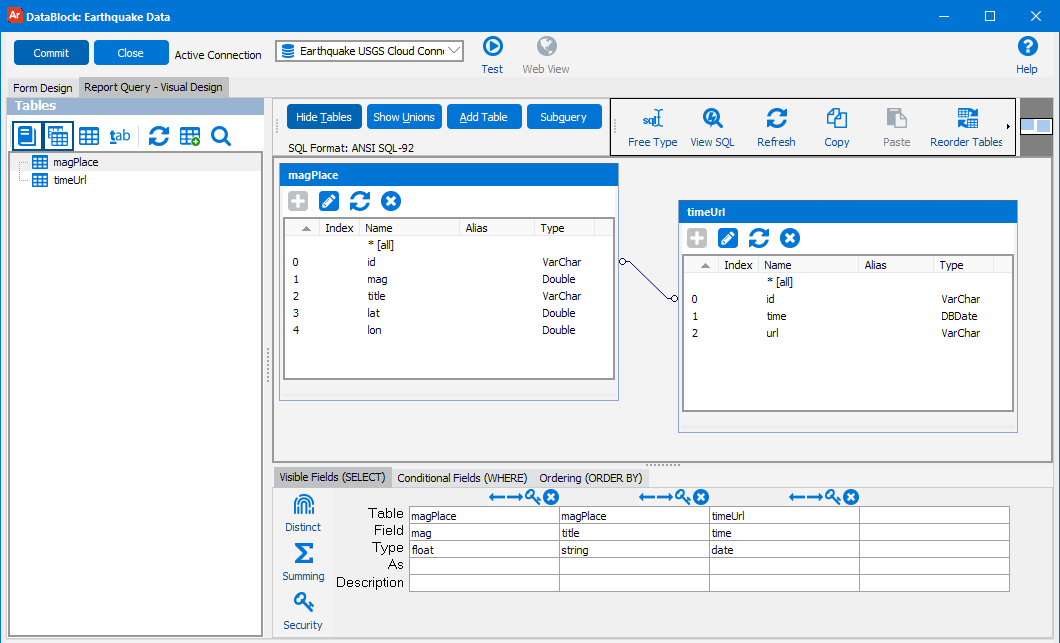
You can use the connection data anywhere that you use SQL in Argos, such as for the report query and in dashboard objects such as list boxes, drop-downs, and charts. If you are using the Visual Designer, the Show Tables button will display the list of tables that were returned by the connection. You can then easily add the desired tables and fields to your query.
Running a report based on the query we just entered shows the data that has been brought over from the Cloud Connector:
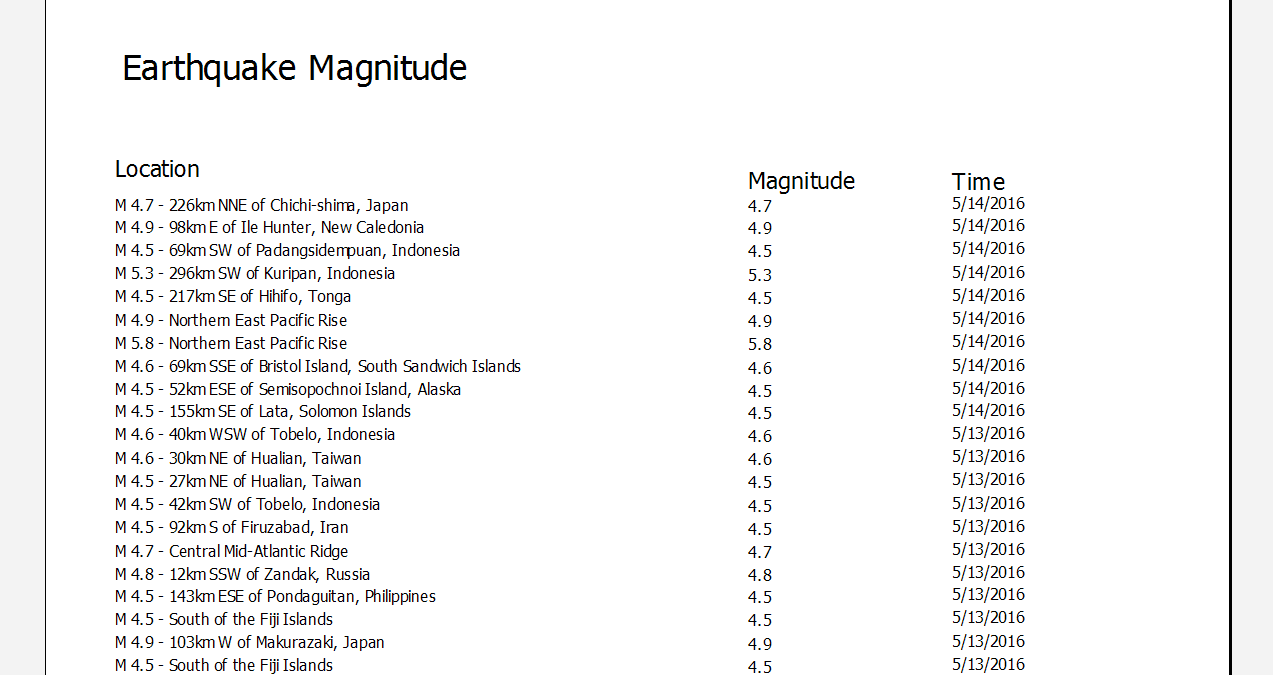
When the Cloud Connector returns a date type field, MAPS is capable of parsing dates using either Julian or ISO 8601 formatting. If the date is in a different format, it may display as "12/30/1899" or possibly another incorrect date. If needed, you can use SQL to convert dates to a more appropriate format. For example, in the Visual Designer you can create a calculated field to cast the date as a varchar and then treat it as a string or perform further conversion as desired.
ISO 8601 dates can be in any of the following formats:
- YYYY
- YYYY-MM
- YYYY-MM-DD
- YYYY-MM-DDThh:mmTZD
- YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ssTZD
- YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss.sTZD
'TZD' stands for Time Zone Designator, and begins with a plus or minus using one of the following formats:
- +-hh
- +-hh:mm