APIDirector
The APIDirector module is used to build and send REST API requests. With the APIDirector, any output from FormFusion may now be sent in one or multiple API calls to a specified endpoint.
Configuration
For information on the Execute this Director section, please see the FormDirector page.
Properties
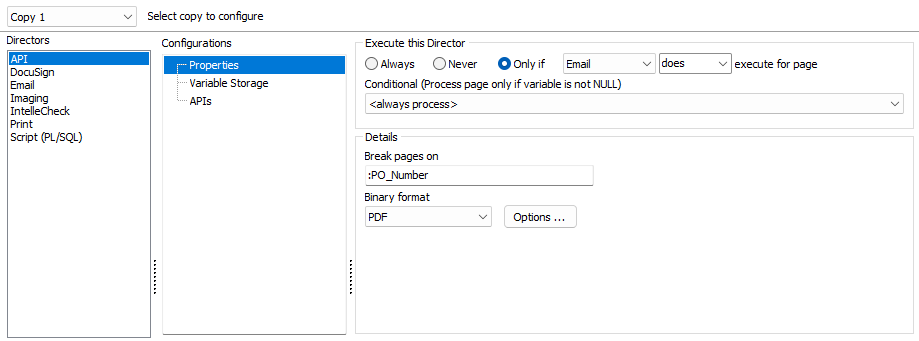
-
Break pages on - (Optional) Enter a string value to use as a page separator so that APIDirector parses the output file into individual files. A MapForm or CaptureForm variable can be entered, with a colon preceding the variable name. In this example, a purchase order number has been mapped with a floating field in MapForm, and is being stored into the :PO_Number variable. This variable will take on a different value for each PO, which makes it an ideal variable to “break” the input file into individual PDFs. Note how the colon before the variable name tells FormFusion that it is a variable and not plain text.
- Binary format - Select the output format for the file: None, Unformatted, or PDF. PDF output has additional options such as document information, encryption, and file compression. Unformatted prints the original input file. This is useful if you want to keep a record of the original input file. None results in no output. This allows you to make API calls without producing an output file.
Important note: The variable used to break the output into individual files must be present on every page of the output file, and positioned consistently from page to page. FormFusion creates a new PDF every time this value changes, including if it is blank.
To generate one output file (do not break pages), leave the Break pages on field blank.
Variable Storage
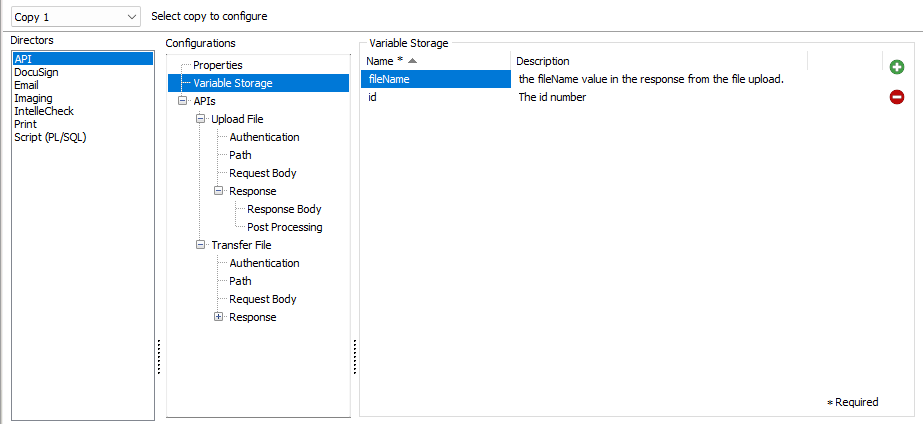
The APIDirector uses its own variable storage. Variables created here must be manually typed as they will not be available from the Variables Reference list. In addition, the variable names created here cannot match any variables names that exist in the Variables Reference list. They may only be used within the APIDirector for referencing other API responses for input with an HTTP Request.
Use the plus and minus buttons on the right side of the window in order to create or delete variables.
- Name - Input the required name of the variable being created.
- Description - Set a custom description for your variable.
The variables stored here are only used when creating multiple, or subsequent, API calls. The variables are only valid once a value has been mapped to it in post-processing via the Response Body tab.
Note: All variables in the APIDirector are strings.
APIs
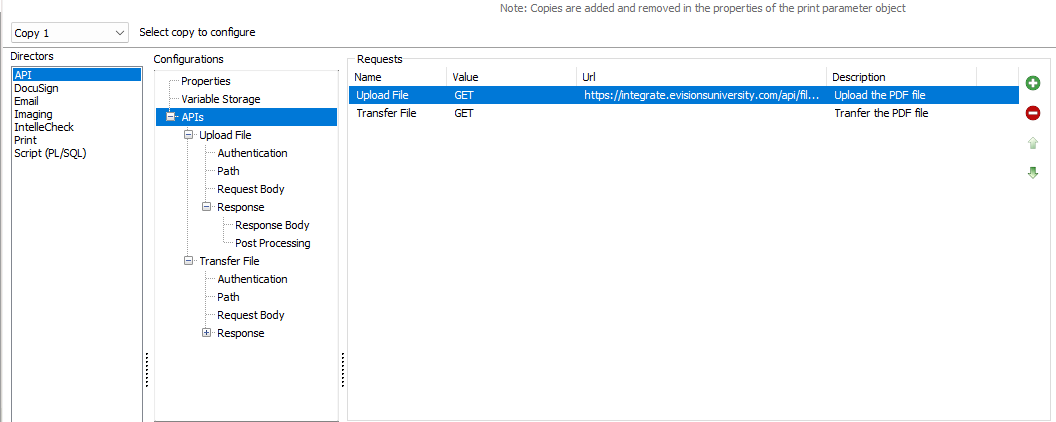
The plus and minus buttons on the right side of the window are used to add and delete requests, while the arrow buttons may be used to reorder the list. Reordering the requests here changes the order in which the requests are called. Depending on the Post Processing settings of each request this may change the outcome as some variables are reused for multiple requests.
New Request
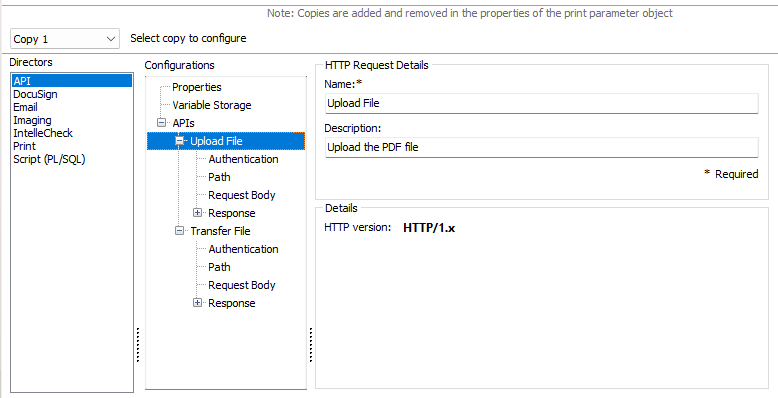
On the New Request tab, you may rename your request and add a description. The Details field shows what version of HTTPs is being used for the request.
Note: Renaming the request here will also change the name of the item in the tree.
Authentication
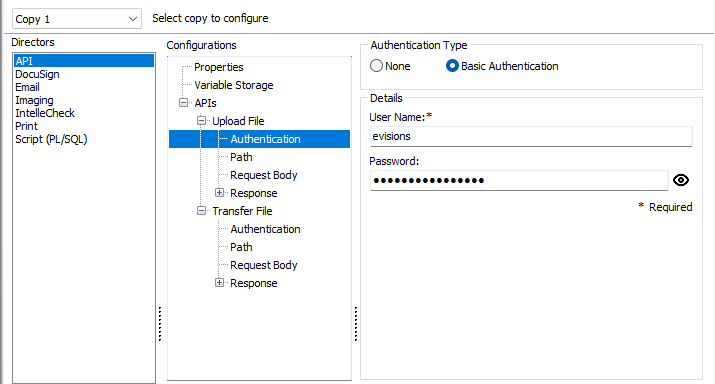
On the Authentication tab, you may choose the request's authentication type. The default option is None, but selecting Basic Authentication reveals the Details pane where a User Name is required (the Password may also be set, but it not required) in order to run the API call.
Path
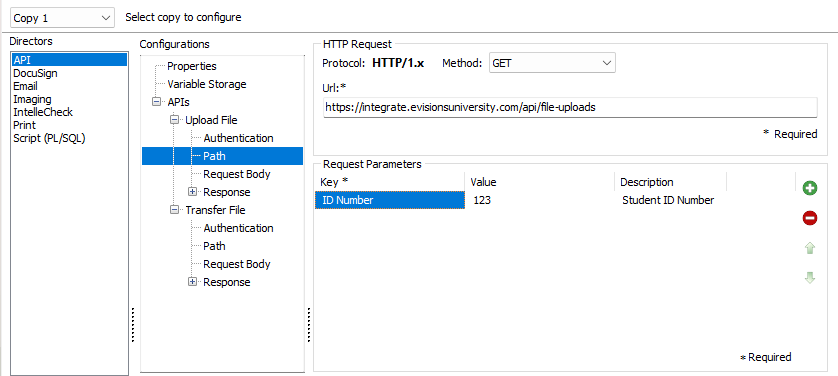
The request's destination is configured on the Path tab.
- Method - The APIDirector supports both GET and POST HTTP Request methods. Select GET when the request is intended to retrieve data from an endpoint, or POST when the request is intended to send or upload data to an endpoint.
- URL - The destination of the request. The destination URL can be provided by the API vendor.
Under the Request Parameters field, Key and Value pairs are added to the URL in order to further configure and refine the destination of the API call.
- Key - The identifier of the value being passed into the request (example: Date, ID, etc).
- Value - The value or measured data of the key being passed (example: ID number 12345).
- Description - A custom description of the key and pair value being added to the URL.
Request Body
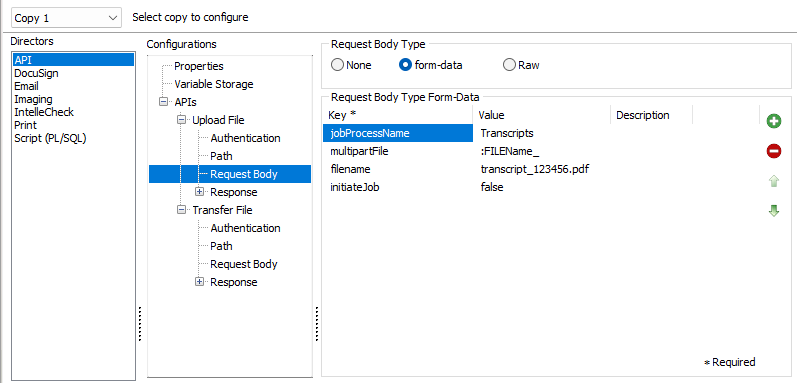
The default option is None, however the body of the request supports form-data and Raw data types.
Under form-data, key and value pairings may be added in the same way they were on the Path tab. Values added here however are passed into the body of the request instead of the URL destination.
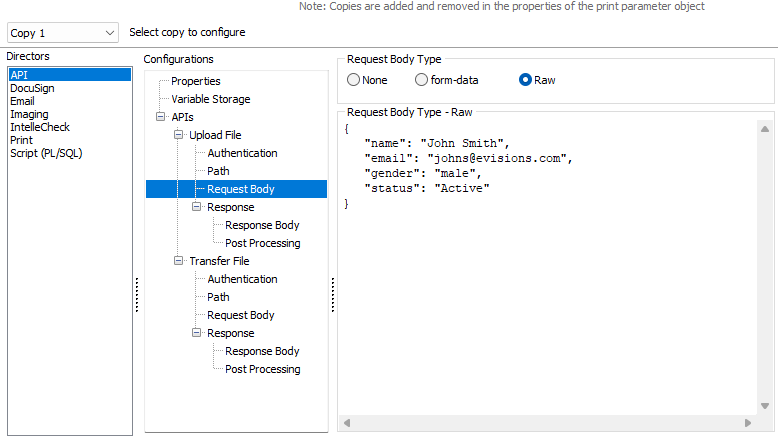
The Raw data type option is used when more complex levels of data need to be passed to the request body.
Note: JSON is the only format supported for the Raw body type.
Response
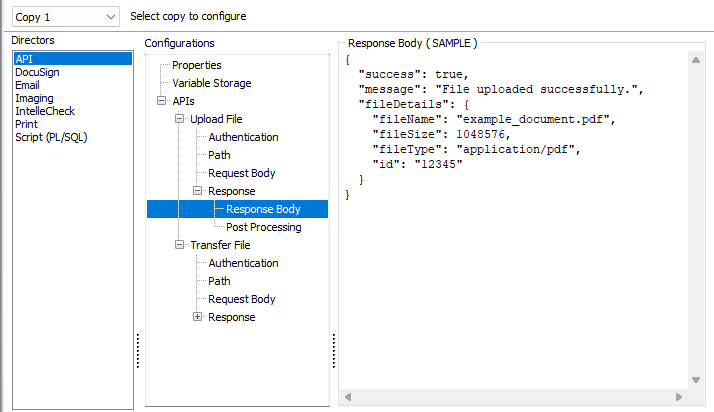
On the Response Body tab, a sample API call response may be posted here if desired. This may be useful when samples are needed for reference at a later time.
Post Processing
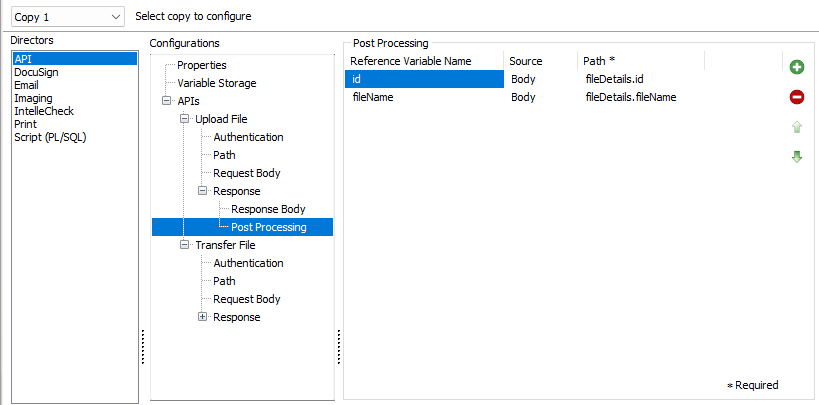
The Post Processing tab is where values are assigned to reference variables. Variables may be added or deleted using the plus and minus buttons on the right side of the pane. Variable assignment order can be modified by using the arrow buttons on the right side of the pane. The order here is only for reference of desired variable assignments or readability order.
- Reference Variable Name - The name of the variable to be given a value. This may only be populated by variables from the APIDirector variable storage.
- Source - Where the value is coming from.
- Path - The specific data from which the value is coming from (the source within the source). In this example, the path is telling us which part of the body is mapping value to the variable.
Variables may only be reassigned within a single Post Processing request one time, however they can be reassigned in any other Post Processing request area again.
The Path field for Post Processing variable assignment supports dot/bracket JavaScript notation for setting the path to the value of the Post Processing variable. This can be useful for situations where the JSON key names contain spaces or special characters.
For example, the LastName value may be set using any of these formats:
data.Students[0].LastName
or,
["data"]["Students"][0]["LastName"]
or,
data.Students[0]["LastName"]
A backlash may be used for escaped notation (hex, octal, unicode, new line character, etc.). Since variables can be used in the path (using colon + varname), and the variable name converter also supports a backslash as an escape character, any escape characters in the path that are intended to remain after being processed by the variable name converter need to be double escaped.
Example: if we have Name. X, where there is a space between Name. and X, in order to access that field, the bracket notation would be: data.Students[0]["Name. X"]
An example of HEX escaped notation would be similar: data.Students[0]["Name.\x20X"] where \x20 is the "space" character in HEX.
Within FormFusion, the backslash needs to be escaped so it can make it through the variable converter.
Second Request
Some API calls are a two-step process and may require a second request (example: uploading a file, and transmitting the data). Subsequent requests may be filled out in the same manner as the first, and any variables created in post-processing of your first request may be easily used in the second.